.jpg)
Anatomy labs have always been an important part of education, but they also face several challenges:
1. Limited Specimen Resources: Anatomy teaching relies on a large number of animal specimens, which are not only costly to obtain but also difficult to preserve and have a short lifespan, leading to resource waste.
2. Ethical Controversies: With increasing awareness of animal protection, the use of live animals or specimens in teaching is facing growing ethical criticism, particularly within educational institutions and in public discourse.
3. Operational Risks: The anatomy process involves sharp tools, preservatives, and biological samples, posing safety and health risks to both students and teachers.
4. Observational Limitations: Once anatomical specimens are processed, they are difficult to reconstruct, preventing students from repeatedly observing key areas, especially fine structures, significantly diminishing the learning effect.
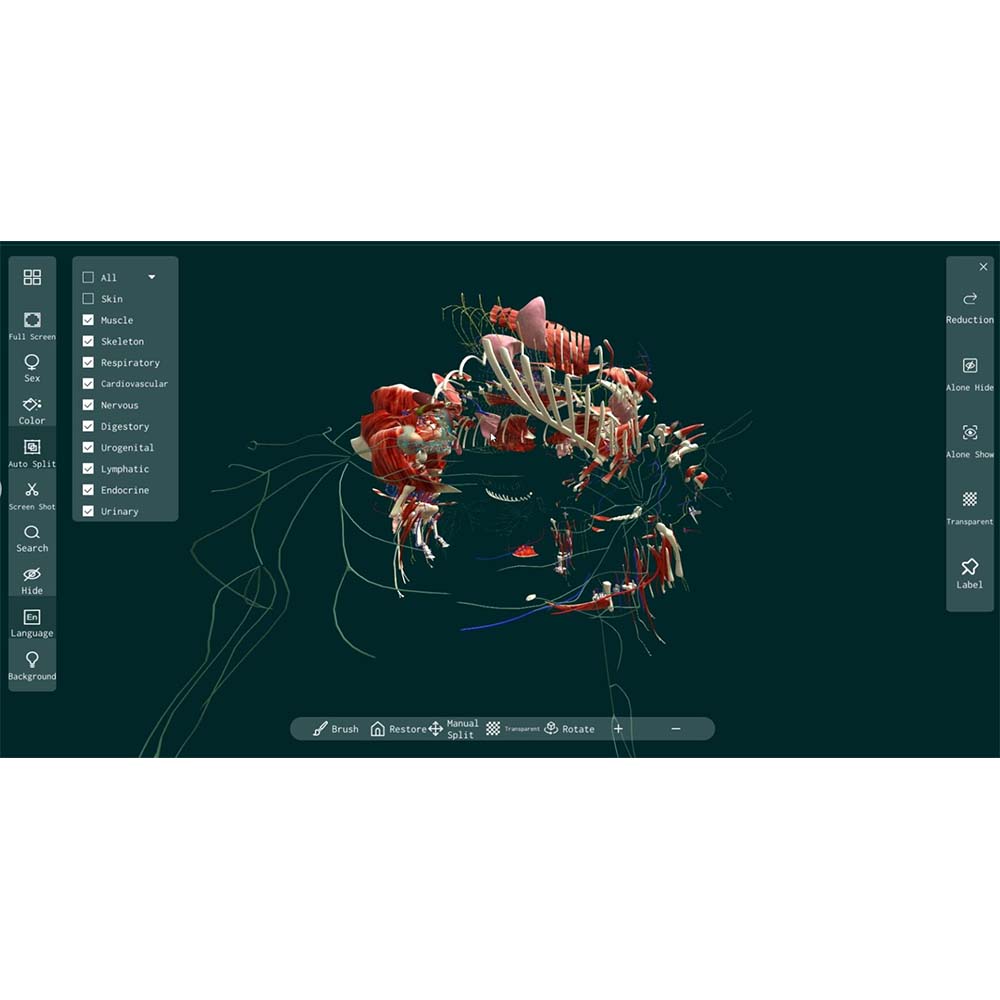
The emergence of virtual simulation anatomy teaching systems has completely changed the model of anatomy teaching. Through advanced 3D modeling and virtual reality technology, this system provides students and teachers with more flexible, safe, and innovative learning tools.
1. High-Precision 3D Models
The virtual simulation system reproduces the anatomical structures inside an animal's body using realistic 3D models, with each organ, muscle, blood vessel, and even tiny neural network clearly visible. Students can zoom, rotate, and decompose the model to observe details that are normally inaccessible.
2. Immersive Interactive Experience
Through VR devices, students can "enter" the animal's body, operate virtual dissection tools, and simulate the real dissection process. Whether it's cutting, separating, or reassembling, all operations can be completed in real time, greatly enhancing learning engagement and interest.
3. Repeatable Learning
Traditional specimen dissection is irreversible, while the virtual system allows students to "practice" multiple times and easily "reset" the anatomical model. This repetitive process allows students to gain a deeper understanding of complex anatomical structures and physiological processes, consolidating their learning outcomes.
4. Environmentally Friendly and Ethical
Virtual simulation teaching eliminates the need for real specimens, reducing reliance on animals and avoiding the environmental impact of specimen disposal. This teaching model aligns with the high ethical and environmental requirements of contemporary education, making it particularly suitable for institutions promoting sustainable development.
5. Interdisciplinary Applications
Virtual simulation technology is not only applicable to teaching but also to scientific research, veterinary clinical training, and medical simulations. For example, by dynamically simulating heartbeats or lung expansion, students can better understand organ function, further expanding the applications of anatomy.
With the popularization of virtual simulation technology, anatomy laboratories are transforming from traditional models to digital and intelligent ones. Virtual simulation teaching systems not only overcome problems such as specimen shortages, ethical controversies, and operational risks but also make the learning process more flexible and efficient. This emerging technology not only simplifies anatomy learning but also opens up more possibilities for biology and veterinary education.